Climate of Australia
Australian Weather Guide
Australian Weather Guide
The climate of Australia can vary a great deal from place to place, although in summer it’s basically hot everywhere in varying degrees (little weather joke there)
Australia is an essentially arid continent, with 80% of the land having a rainfall less than 600 millimetres per year and 50% having even less than 300 millimetres per year.
Australia is in the southern hemisphere so our seasons are opposite from the northern hemisphere; this means that Christmas in Australia is in summer when it’s hot, and summers can get quite a bit hotter than they do in the northern hemisphere.
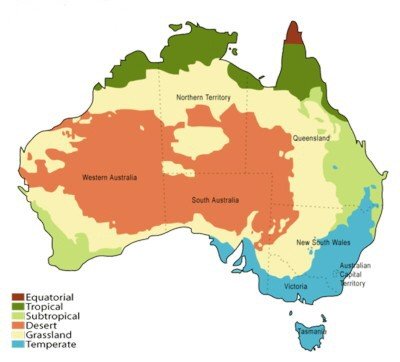
Graphic from Wikipedia under
GNU Free Documentation License
Seasons in Australia are:
Summer: December to February
Autumn: March to May
Winter: June to August
Spring: September to November
The weather in Australia can range from the below zero temperatures of the Snowy Mountains region to the extreme heat of the northwest.
The tropical north regions of Australia have high temperatures and humidity and distinct wet and dry seasons.
The centre of the country is the dry, desert regions with daytime temperatures that are high, and low amounts of rain.
The southern regions of Australia are temperate with temperatures ranging from hot to cold with moderate rainfall.
The dry climate of Australia, especially in the northern region leads to droughts, heat waves and bushfires. Bushfires are a major cause of concern in Australia.
Where I live at the moment, in Adelaide, the temperature in summer can reach 40 degrees Celsius or over a number of times, sometimes for days in a row – not fun!
I’ve lived all over Australia, from the bush to Sydney, Brisbane, Perth and Adelaide, and the weather is different in all these places from the dry heat of the desert to the humidity of Brisbane.
I've included a Celsius to Fahrenheit conversion table below for those people who understand Fahrenheit more as all temperatures in this site are in Celsius.
Celsius to Fahrenheit Conversion Table
| °Celsius | °Fahrenheit | °Celsius | °Fahrenheit |
| 50 | 122 | 10 | 50 |
| 45 | 113 | 5 | 41 |
| 40 | 104 | 0 | 32 |
| 35 | 95 | -5 | 23 |
| 30 | 86 | -10 | 14 |
| 25 | 77 | -15 | 5 |
| 20 | 68 | -20 | -4 |
| 15 | 59 | -25 | -13 |
If you would like to know more about the climate of Australia's different states and territories, including the average temperatures of the capital cities, or you want to check out some interesting and extreme weather facts about Australia, just click on the links below.
New South Wales climate is broad from the mild Sydney weather to the dry heat of the bush in the north western corner of the state.Victoria climate is also broad despite its small size but the southern position of Victoria means it tends to be a bit cooler and wetter.
Queensland climate due to it’s size has a wide variation, from the tropical coasts in the north to the highlands of the south east, were snow has fallen.
South Australia climate varies from the mild wetter regions of the south east coast and Mount Lofty Ranges to the hot and dry interior.
Western Australia climate is one of the most diverse in the country due to its size, from the tropical north to the temperate south west coastal areas.
Tasmania climate is temperate maritime with four distinct seasons, from the warm sunny days of summer to the sudden storms of winter.
ACT and Canberra climate is relatively dry and continental with marked seasonal and daily temperature changes.
Northern Territory climate is in two zones, the tropical north which includes Darwin, and the desert environment of Central Australia.
Weather Facts and climate extremes: highest maximum temperature, lowest minimum temperature, longest heatwave and much more.
Return from Climate of Australia to Australian-Information-Stories home page


